Since the signing of the Ukraine-EU Association Agreement, Ukraine has implemented numerous reforms across almost every aspect of life. However, many essential areas remain outside the reform process. One such area is medical education, which is crucial for fostering a knowledge-based economy.
The COVID-19 pandemic and antibiotic resistance crisis highlighted existing weaknesses in the Ukrainian healthcare system. National services responsible for controlling biological threats underwent multiple reforms, leading to the creation of the Public Health Centre as an upgraded institution. Nevertheless, there is a significant shortage of graduates able to coup with biological threats.
Despite the significant changes introduced by the 2015 law on higher education in Ukraine, which led to the renewal of educational programs, a comparison of biomedical education in Ukraine and Europe highlights an urgent need to modernize and align existing curricula with EU standards. Integration of EU practices and legislation into Ukrainian medical education programs will enhance graduates’ readiness to address global biological threats and prepare them to work effectively anywhere in the world.
Additional challenges for higher medical education in Ukraine include the quarantine measures and russian aggression. To address the aforementioned issues, we implemented EU norms and legislation on biosafety and biosecurity into the education of students mastering the field of biomedicine, utilizing prominent European educational practices and techniques.
The purpose of this article is to demonstrate how the implementation of innovative technology allows to increase the awareness of medical students with the EU legislation on biosafety and biosecurity.
In 2022-year, Public Health Department of Sumy State University started to realize the elective course “European regulations in biosecurity and biosafety considering global challenges” as a part of Jean Monnet module with the implementation outstanding practices and innovative methods into the medical student education.
Distance learning technology has been widely adopted in education since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although there were a lot of discussion on advantages and disadvantages of this study method, it became an integral part of higher education. Therefore, we actively utilized it as part of the integration of outstanding methods and approaches from EU higher education into the training of medical students [1].
Distance learning incorporates the use of electronic textbooks, interactive whiteboards, and advanced computer programs to monitor and assess knowledge levels [1]. As part of the Erasmus+ Jean Monnet Module project, we developed educational materials that were integrated into the university's e-learning platform, ensuring access to information for all participants in the educational process. Distance learning for students was conducted through independent study of educational materials uploaded to the MIX educational platform.
To achieve optimal results during practical classes, we employed active group learning techniques, such as team-based learning. During practical classes, students completed group assignments in the form of problem-based tasks, followed by presentations of the results and subsequent group discussions [2]. The case method formed the basis of student discussions, promoting the development of both hard skills and soft skills formation among the participants. The development of teaching material indirectly enhanced the pedagogical skills of university staff, which was an integral achievement of the Jean Monnet project. This changed the nature of the interaction between the teacher and the student of higher education, orienting them to equal collective educational work.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented approaches, we conducted a student survey and analyzed the students' scores at the end of the course. In 2023 year, 50 students attended the course and 39 students were reviewed within the survey.
All surveyed students attended most classes in the discipline, and 82.1% chose the course independently. All respondents indicated that they liked the course and their awareness in the EU norms and practices on biosafety and biosecurity was raised.
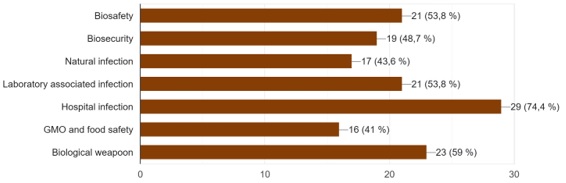
When the participants were asked indicate the most interesting topic for them, the majority commented that hospital infection was the most interesting topic (fig1.).
Figure 1. – The answers to the question -what is the most interesting topics?
The participants overall demonstrated positive attitude to team based learning. 97.4% of those who were interviewed indicated that they like this form of educational methodology. In all cases, the informants reported that they would advise the course to other students.
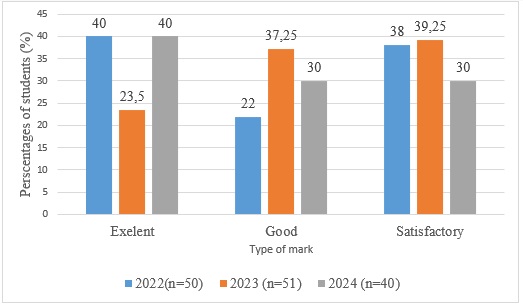
In the next step, we evaluated the scores of students who attended the elective course.
Figure 2. – The distribution of the students marks during 2022-2024 years
Two thirds of students received an excellent or good grade, which confirms a high level of knowledge perception and a positive attitude to the educational material.
All mentioned above confirms the assumption that the problem based learning and team based learning approaches meet the needs and expectations of students as much as possible. These aproacheas are student-oriented and promote personality development. In addition, this form of education allows students to gain a high competitive status in the labor market. When using this type of interaction between a student and a teacher, the role of the latter is not a mentor but an assistant who promotes the self-development of students. These educational technologies are widespread in the educational space of the European Union. They gain high popularity in Ukraine, as these approaches meet the modern requirements of training new specialists.
Biside this implementation of such educational methods will stimulate formation of critical thinking technology. It allows to increase the efficiency of information perception as well as rise interest in the studied material.
Conclusion
The implementation of problem-oriented learning and team learning helps to increase the awareness of students in higher medical institutions in Ukraine regarding the practice and legislation of the EU on biosafety and biosecurity. These methods enhance the effectiveness of learning and students’ motivation.
References:
1. Deborah Bedoll, Marta van Zanten, Danette McKinley. Global trends in medical education accreditation. Hum Resour Health. 2021; 19: 70. Published online 2021 May 20. doi: 10.1186/s12960-021-00588-x PMCID: PMC8136216
2. Anderson E., Schiano B. Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide. HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL PRESS, 2014. 304 p. David, Thomas (2003). Case Studies for ELT: a source of motivation. Cahiers de l’APLIUT, Vol. XXII № 2, 2003. Retrieved from https://journals. openedition.org/apliut/3730?lang=en
Acknowledgments: We highly appreciate the finansial support given by Erazmus + JM Module project EuroBioSec 101048202 - GAP-101048202.
|